Bits and Bytes
Bits are simply 0s and 1s and that's all the language our machine understands. But in larger picture how do we understand this when we are programming? Trying to troubleshoot production system?
8 bits = 1 byte
- Bit: The smallest unit of data in computing, representing either a 0 or 1
- Byte: A group of 8 bits
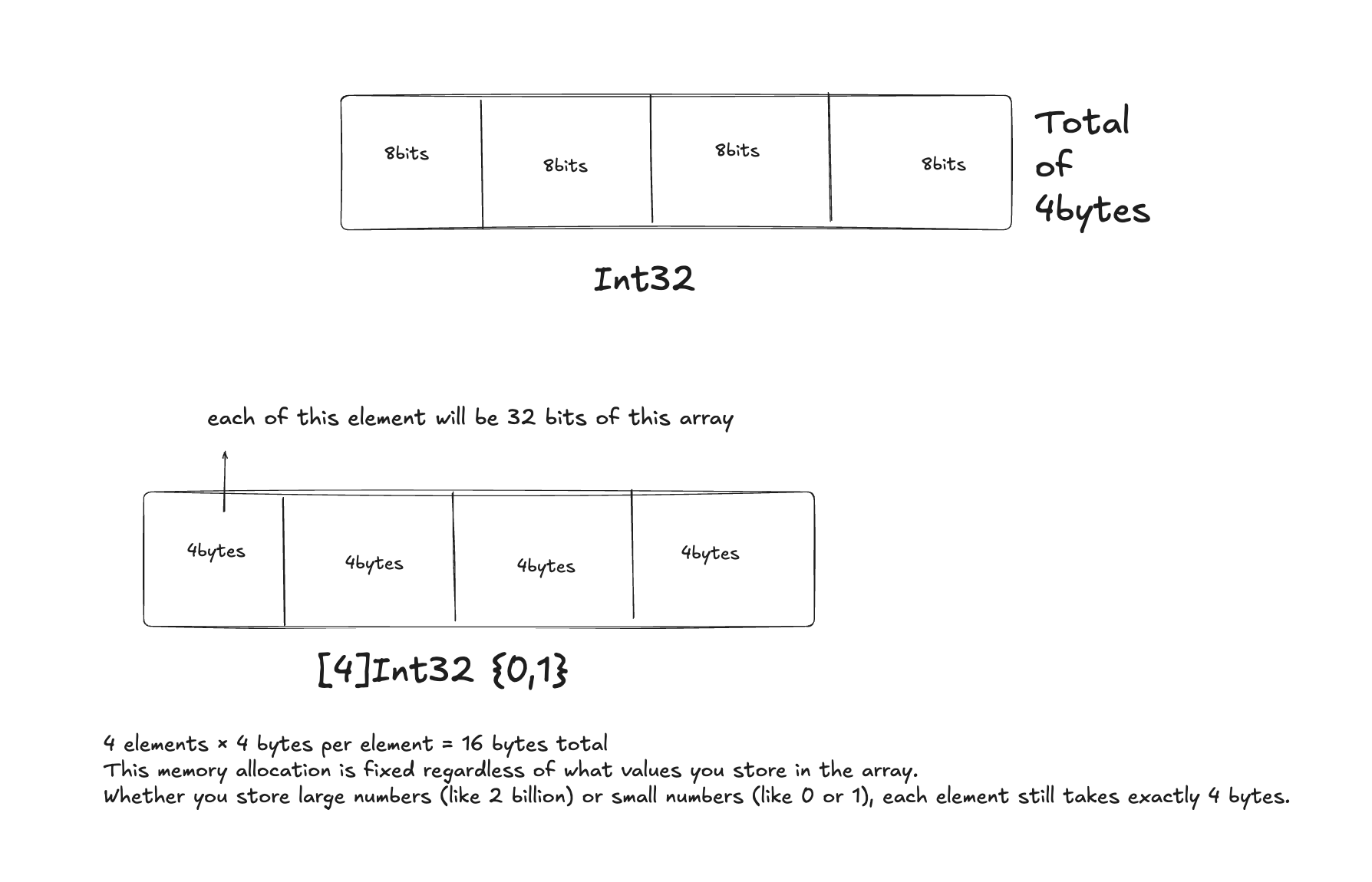
Arrays and Memory
When you see "int32" (32-bit integer):
- This means the integer uses 32 bits (or 4 bytes) of memory (since 32 ÷ 8 = 4)
- When you have an "int32 array" with n elements:
- Each element takes 4 bytes (32 bits)
- The entire array takes n × 4 bytes of memory
Common Data Type Sizes
- int8: 1 byte (8 bits) - can store values from -128 to 127
- int16: 2 bytes (16 bits) - can store values from -32,768 to 32,767
- int32: 4 bytes (32 bits) - can store values from about -2.1 billion to 2.1 billion
- int64: 8 bytes (64 bits) - can store much larger values
Memory Unit Conversions
- 1 bit = A single binary digit (0 or 1)
- 8 bits = 1 byte
- 1,024 bytes = 1 kilobyte (KB)
- 1,024 KB = 1 megabyte (MB)
- 1,024 MB = 1 gigabyte (GB)
With 1 GB of memory, you could store: - Approximately 268 million int32 values (since each int32 is 4 bytes)
- About 1 billion characters in a string (using 1 byte per character for ASCII)
When discussing computer memory or storage, we typically use bytes as the fundamental unit, not bits. Bits are more commonly referenced when discussing data transfer rates (like internet speeds, which are often measured in Mbps - megabits per second).
